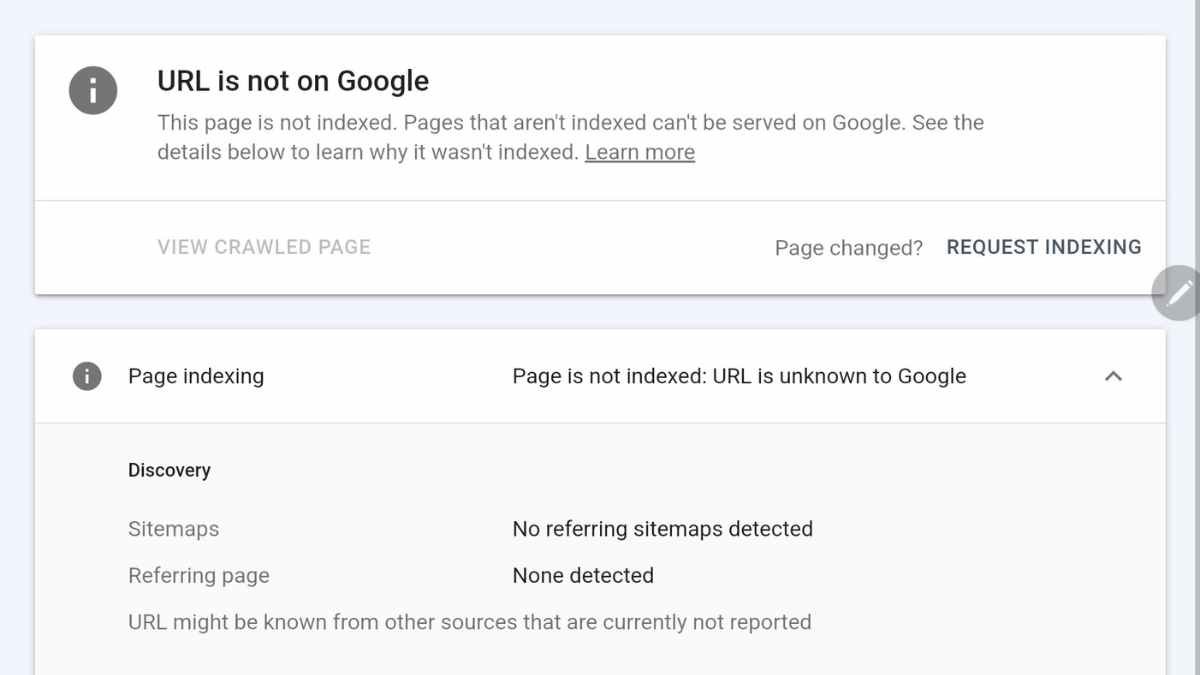
A non-indexed page is a webpage that search engines like Google do not include in their search results. This can be due to technical issues, strategic decisions, or intentional actions.
Understanding what a non-indexed page is and how it affects your website’s visibility in search engines is crucial for website owners and digital marketers. A page that is not indexed will not show up in search engine results, which can hinder the page’s ability to drive organic traffic.
Let’s dive deeper into what a non-indexed page is, why it happens, and how you can fix it if needed.
What Is A Non-Indexed Page – Overview
A non-indexed page refers to a webpage that search engines have chosen not to store in their index.
When a search engine like Google crawls a site, it makes decisions about which pages to store in its database. Only the pages that are stored, or “indexed,” are available to show in search results.
Indexing is essential for a page to appear in search engine results. If a page is not indexed, search engines essentially treat it as if it doesn’t exist, which can have serious implications for SEO.
Search engines aim to index high-quality, relevant, and valuable content. Pages that do not meet these criteria, or that have been deliberately marked as non-indexable, are excluded.
Read Also: What Is Rapid URL Indexer?
How Search Engines Work With Indexed and Non-Indexed Pages
Search engines follow a multi-step process to manage web pages: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Crawling involves sending out bots (also known as spiders or crawlers) to explore pages across the internet. When a crawler visits your website, it analyzes the structure and content of each page, determining if it should be included in the search engine’s index.
Once a page is crawled, search engines decide if the page is worth indexing. Indexed pages are stored in a search engine’s database and are eligible to appear in search results based on relevant user queries.
Non-indexed pages, however, are excluded from this database. This could happen for various reasons, such as poor content quality or directives from the website owner (e.g., the use of a “noindex” tag).
Why Would A Page Be Non-Indexed?
A page can be non-indexed for several reasons, either due to technical issues or strategic decisions by the website owner.
Technical Issues
One common reason for a page being non-indexed is technical issues. For instance, if a website’s robots.txt file blocks a search engine from crawling specific pages, those pages won’t be indexed.
Another technical reason could be the presence of a noindex meta tag on the page’s HTML code, which explicitly tells search engines not to index the page.
Other factors like server issues, duplicate content, or broken links may prevent a page from being indexed. For example, if Google detects that two pages have very similar or identical content, it may choose to index only one and exclude the other to avoid duplication in its search results.
Strategic Reasons
Sometimes, website owners may intentionally prevent certain pages from being indexed for strategic reasons. Pages like login forms, testing pages, or those that are part of a staging site are often marked as “noindex” to avoid unnecessary clutter in search engine results.
Additionally, pages that provide little to no value (thin content) or pages with sensitive information that should remain private (such as an internal employee directory) are often purposefully excluded from being indexed.
Impact of Non-Indexed Pages On SEO

Having non-indexed pages on your site can impact your SEO performance in both positive and negative ways, depending on the situation.
Negative Impacts
In cases where a page is unintentionally non-indexed, it can negatively affect your site’s visibility.
Pages that could potentially rank well but are not indexed will not appear in search results, depriving you of organic traffic and potential customers. This can also skew data in your analytics tools, making it harder to assess the performance of your content.
Additionally, if a significant portion of your website is non-indexed, it can lower the overall domain authority of your site, signaling to search engines that your site may not be providing valuable information.
Positive Impacts
However, non-indexing can also be a strategic decision. Not every page on your site needs to be indexed, especially if it doesn’t provide value to search engine users. For example, internal policy documents, outdated pages, or archived content may not need to appear in search results.
In these cases, keeping certain pages non-indexed helps focus a search engine’s attention on your more valuable content, which can improve the overall ranking and SEO performance of your important pages.
How To Identify Non-Indexed Pages?

To identify non-indexed pages, several tools can help. One of the most common tools is Google Search Console, which allows you to see which pages Google has crawled and indexed, as well as those that remain unindexed. It also highlights errors and reasons why specific pages might be excluded.
Another useful tool is Screaming Frog, a website crawler that helps you audit your site for SEO issues, including identifying non-indexed pages and uncovering issues like broken links, duplicate content, or improper noindex tags.
By conducting regular site audits, you can stay ahead of non-indexing issues and ensure that your most important pages are always visible to search engines.
How To Fix Non-Indexed Pages?
Once you’ve identified non-indexed pages, it’s essential to fix them, especially if their exclusion from search results is unintentional.
Fixing Technical Problems
Start by fixing any technical issues that may be causing the non-indexing.
For example, if a page is blocked by a robots.txt file or a noindex meta tag, remove those directives to allow the page to be crawled and indexed. Also, ensure that the page’s content is original and not duplicative of other pages on your site.
Fixing broken links or updating your sitemap to include important pages are other steps that can help correct non-indexing problems.
Improving Page Quality
If the content on a non-indexed page is thin, outdated, or irrelevant, consider improving the page’s quality by adding more useful, unique, and keyword-optimized content. This will increase the chances of the page being indexed and ranking well in search results.
Also, ensure that your page’s load speed is optimized and mobile-friendly, as search engines prioritize indexing pages that provide a better user experience.
Use Alternatives – Indexing Tool Rapid URL Indexer
- Rapid URL Indexer Vs. Indexification
- Rapid URL Indexer Vs. IndexMeNow
- Rapid URL Indexer Vs. Omega Indexer
- Rapid URL Indexer Vs. OneHourIndexing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is my page not indexed by Google?
Your page may not be indexed due to technical issues (e.g., noindex tags or robots.txt exclusions) or low-quality content.
How do I make my page indexed?
Ensure your page is not blocked by any technical barriers like a noindex tag and improve the quality of the content on that page.
Can a non-indexed page still get traffic?
No, non-indexed pages won’t appear in search results, but they may still receive traffic from direct links, social media, or email campaigns.
Is non-indexing bad for SEO?
It depends. Non-indexing can hurt SEO if done unintentionally, but it can be useful in specific cases, like hiding irrelevant content.
Conclusion – What Is A Non-Indexed Page?
In conclusion, non-indexed pages are those excluded from search engine results either intentionally or unintentionally.
While indexing is crucial for SEO success, there are times when non-indexing can be strategic.
Regularly auditing your website for non-indexed pages and fixing any technical or content issues can help you maintain visibility and improve your overall SEO performance.
Always focus on indexing high-value, relevant content to keep your website ranking effectively.